Introduction:
Research from the Harvard Business Review shows that businesses that understand their customer base and market segments are 60% more likely to succeed in their marketing campaigns. Implementing the STPD strategy in your marketing efforts not only helps you engage your audience but also provides a roadmap for sustained growth.
In this article, we’ll guide you through the process of implementing the STPD strategy in your marketing plan, breaking down the theoretical underpinnings and practical steps you can take to craft your own STPD strategy.

1. Step 1: Define Your Market – The Foundation of Your Strategy
The first step in the STPD model is to define your market. This is the foundation of your strategy, as it helps you understand the overall landscape in which your product operates and sets the stage for segmentation.
-
Total Available Market (TAM): This is the total demand for your product or service across the entire market. It’s the broadest definition of your target market, representing every potential customer who could benefit from your offering. For example, if you sell fitness equipment, your TAM would include anyone interested in improving physical health globally.
-
Serviceable Available Market (SAM): This is the segment of the TAM that your business can target based on your product offerings, geographical constraints, or other factors. If you only ship fitness equipment to North America, your SAM would be the people in North America interested in fitness equipment.
-
Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM): This is the realistic subset of your SAM that you can capture with your marketing efforts, given your resources and competition. SOM takes into account factors like your current brand awareness, distribution channels, and marketing budget.
How to Implement:
-
Gather Data: Use industry reports, market research, and internal customer data to define your TAM. Public sources like Statista, government publications, or market research firms like Nielsen can provide insights into market size and trends.
-
Refine Your Focus: Narrow down your TAM into your SAM based on your product’s capabilities and your geographical reach. Consider the size of the audience, the purchasing power, and their willingness to adopt your product.
-
Estimate Your SOM: Assess the market you can realistically reach based on your brand awareness, customer base, and marketing budget. Use competitive analysis tools to understand what share of the market you can capture.
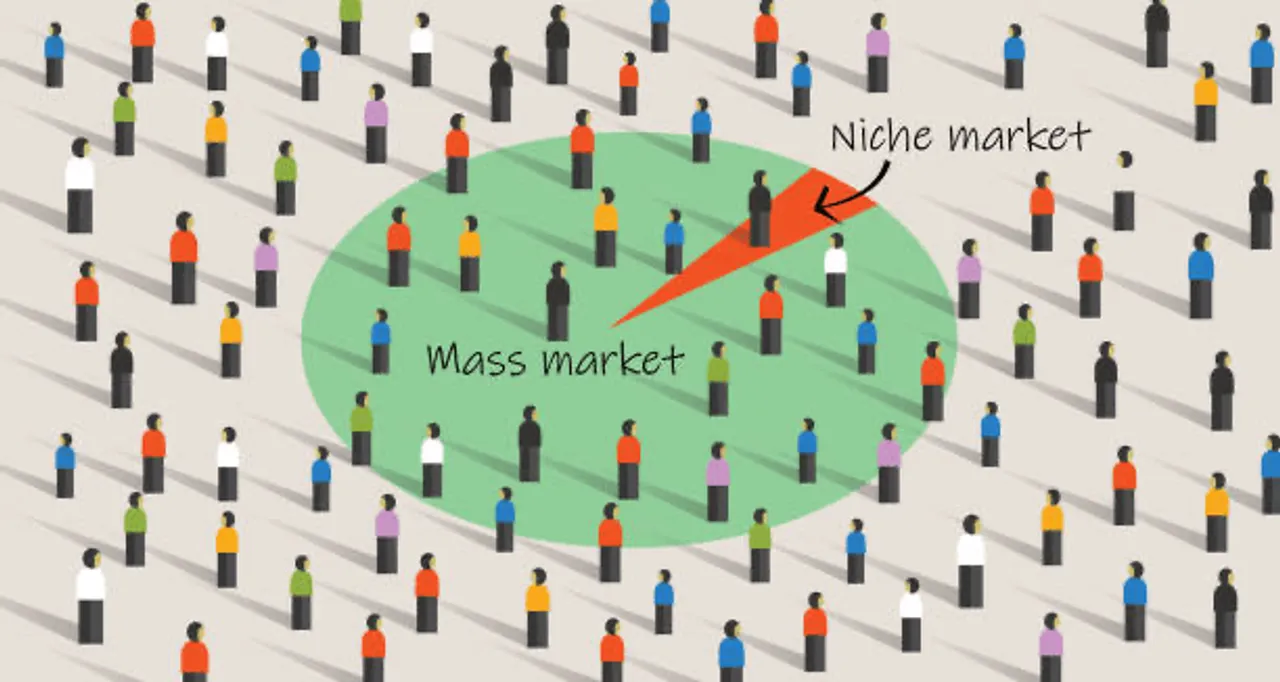
2. Step 2: Create Audience Segments – Identify High-Value Groups
Segmentation is a crucial process in the STPD model because it allows you to break down a broad, undifferentiated market into smaller, manageable groups. These segments consist of customers with similar characteristics or behaviors that align with your product or service. The goal is to tailor your marketing efforts to each group’s unique needs.
-
Demographic Segmentation: Groups people based on characteristics such as age, gender, income, education, and occupation.
-
Geographic Segmentation: Focuses on where customers live, such as country, region, city, or climate.
-
Psychographic Segmentation: Focuses on lifestyle, values, interests, and attitudes of customers. This is often used to understand consumer motivations and preferences.
-
Behavioral Segmentation: Divides the market based on consumer behaviors like buying patterns, product usage, brand loyalty, and engagement levels.
How to Implement:
-
Collect Data: Use surveys, customer data, and insights from tools like Google Analytics to identify key attributes that define your target audience. Social media platforms, like Facebook and LinkedIn, can also help segment audiences based on demographics and behaviors.
-
Segment Your Audience: Divide your audience into distinct groups. For example, if you sell outdoor apparel, you might create segments for hiking enthusiasts (psychographic), buyers in cold climates (geographic), and those with mid to high incomes (demographic).
-
Use Customer Personas: Once you have your segments, create detailed personas to represent each group. This helps you understand the needs, goals, and challenges of each segment.
3. Step 3: Identify the Most Attractive Segments – Make Data-Driven Decisions
Theoretical Overview:
After segmenting your market, the next step is targeting. This step involves evaluating the profitability and attractiveness of each segment, then selecting which to pursue. The goal is to identify the most viable segments where your marketing efforts will yield the highest returns.
Key criteria to evaluate segments:
-
Size: Is the segment large enough to generate meaningful sales volume? A segment may be highly profitable but too small to warrant the marketing investment.
-
Profitability: Is the segment profitable? Evaluate the cost of customer acquisition (CAC) and customer lifetime value (CLV) for each segment. You want to target segments with low CAC and high CLV.
-
Reachability: How easy is it to communicate with and access this segment? If a segment is too fragmented or hard to reach, it may not be worth targeting.
-
Benefit Fit: Does your product or service meet the specific needs of this segment? Segments that are already aware of the benefits of your product will require less effort to convince and convert.
Why STPD is Crucial for Your Business Success
How to Implement:
-
Analyze Each Segment: Using market data and customer behavior insights, assess each segment’s potential. Tools like Google Trends, customer feedback surveys, and CRM systems can help you gather insights.
-
Evaluate Profitability: Compare the costs of reaching each segment against the potential return. Focus on segments that provide the highest ROI.
-
Focus on Reachability: Assess which segments are easiest to target through your marketing channels. If a segment is difficult to access (e.g., through traditional media or expensive digital ads), reconsider whether it’s worth pursuing.
4. Step 4: Position Your Product – Establish Your Brand’s Unique Value
Positioning is about how your product is perceived by the target audience. It defines the place your product occupies in the mind of the customer relative to competitors. A strong positioning strategy ensures that your product stands out and addresses a specific need that is important to your target segments.
Positioning Strategies:
-
Competitor-Based Positioning: Emphasizes your product’s advantages over direct competitors.
-
Price-Based Positioning: Differentiates based on value or affordability.
-
Benefit-Based Positioning: Focuses on how the product solves a particular problem or satisfies a need.
-
Prestige-Based Positioning: Leverages exclusivity and luxury to appeal to affluent consumers.
How to Implement:
-
Develop Your Brand’s Positioning Statement: Write a clear statement that defines your product’s unique value proposition (UVP) for your target audience. For example, “Our high-quality running shoes provide serious athletes with superior comfort and performance.”
-
Identify Key Differentiators: Highlight the features or benefits that set your product apart from competitors. Consider using a product positioning map to visually map out your product’s position in the market.
-
Align with Customer Needs: Ensure that your positioning statement resonates with the core values and needs of your target audience. The goal is to make the customer feel that your product is specifically tailored for them.
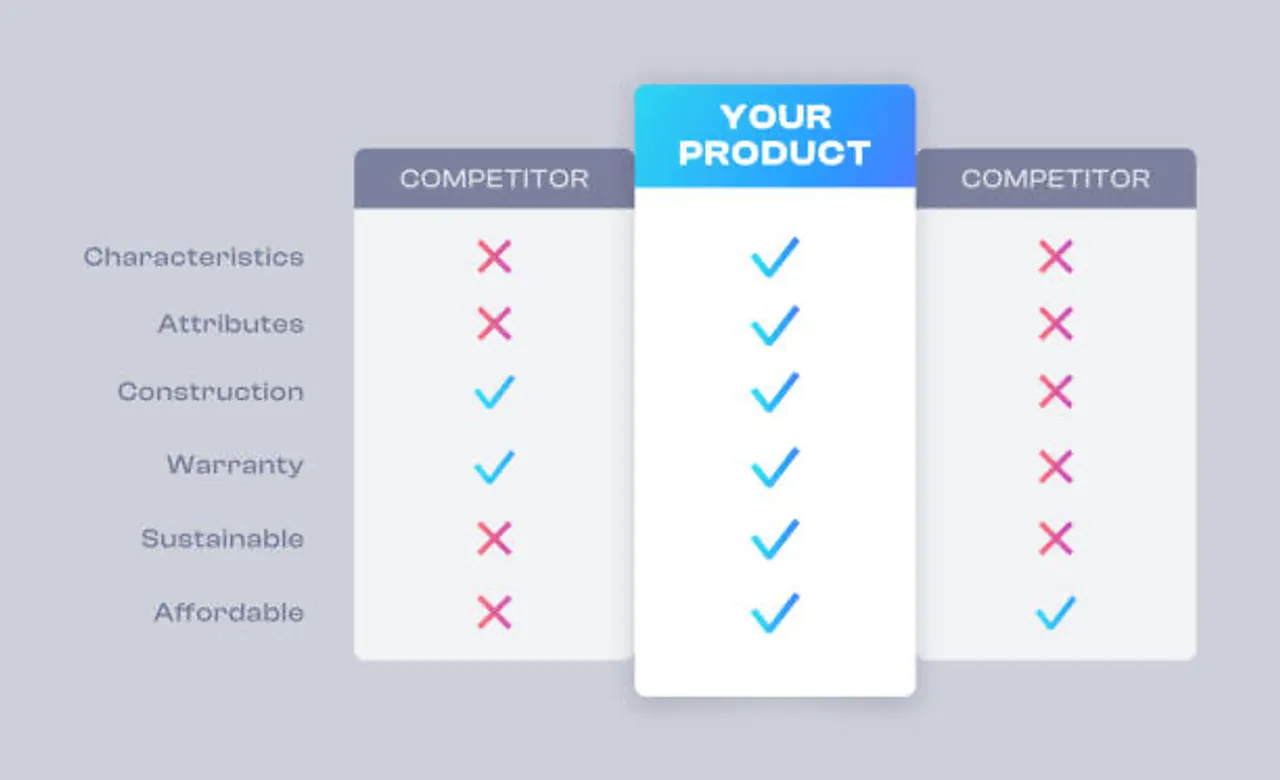
5. Step 5: Differentiate Your Product – Stand Out from Competitors
Differentiation is a strategy that ensures your product is distinct from competing products. It helps to highlight the unique attributes of your offering, whether that’s through quality, customer experience, features, or pricing. Differentiation builds brand loyalty and drives preference.
Key Differentiation Methods:
-
Product Features: Unique characteristics that make your product more valuable.
-
Quality: Offering a superior quality product that exceeds customer expectations.
-
Customer Service: Providing exceptional support and after-sales services.
-
Brand Experience: Creating a memorable customer journey that aligns with brand values.
How to Implement:
-
Identify Unique Features: Determine the core features that differentiate your product. This could include superior functionality, design, or innovation.
-
Emphasize Customer Experience: Focus on providing an exceptional service or experience that competitors lack. For example, consider offering personalized experiences, flexible return policies, or loyalty programs.
-
Create Brand Distinction: Use brand storytelling to convey what makes your product different. Highlight your company’s values and why your product is the best solution.
6. Step 6: Choose Your Marketing Mix – Tailor Your Strategy for Maximum Impact
The marketing mix (4Ps) is a foundational tool used to develop a comprehensive marketing strategy. The 4Ps ensure that all elements of your marketing efforts are aligned and work together cohesively.
-
Product: What are the features, benefits, and services associated with your offering?
-
Price: How will you price your product to reflect its value and attract your target audience?
-
Placement: Where will you sell your product (physical stores, e-commerce, etc.)?
-
Promotion: What promotional tactics will you use to drive awareness and sales (advertising, sales promotions, content marketing)?
How to Implement:
-
Refine Your Product Offering: Ensure that your product meets the expectations and needs of your target audience. Focus on quality, design, and usability.
-
Set the Right Price: Consider the perceived value of your product in your target market. If your positioning is luxury, for example, set a price that reflects exclusivity.
-
Select Distribution Channels: Choose the most effective channels to reach your target audience. Consider both online and offline options, such as e-commerce platforms or retail stores.
-
Design Your Promotions: Create a promotional plan that uses the most effective channels to reach your audience. This could include digital advertising, social media campaigns, influencer partnerships, or email marketing.
Conclusion:
STPD isn’t just a marketing framework; it’s a comprehensive strategy that helps you focus on the most valuable segments and deliver personalized, impactful messaging. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you’ll be able to define your market, segment your audience, position your product effectively, and differentiate it from the competition.